Intro to HTML/CSS
Class 1
Welcome!
Girl Develop It is here to provide affordable and accessible programs to learn software through mentorship and hands-on instruction.
Some "rules"
- We are here for you!
- Every question is important
- Help each other
- Have fun
Welcome!
Tell us about yourself.
- Who are you?
- What do you hope to get out of the class?
- What's one of your favorite websites?
Goals
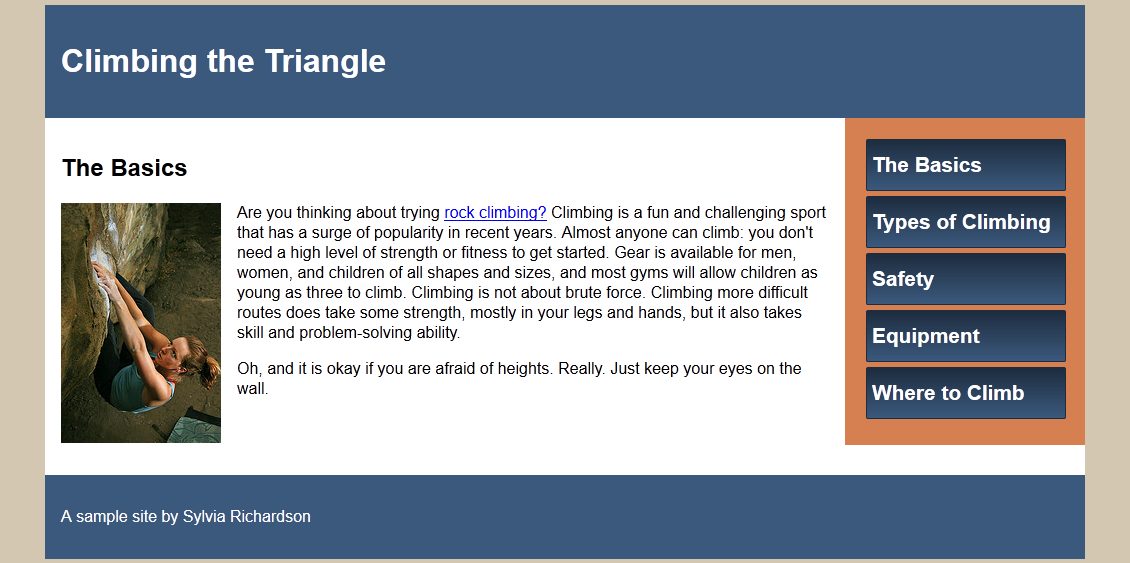
By the end of the class, you will have built a simple site using HTML and CSS which includes images, lists, fonts, navigation header/footers.
What is HTML?
HTML is the markup language that allows us to build websites
HTML is composed of HTML tags that together provide a blueprint for a webpage.
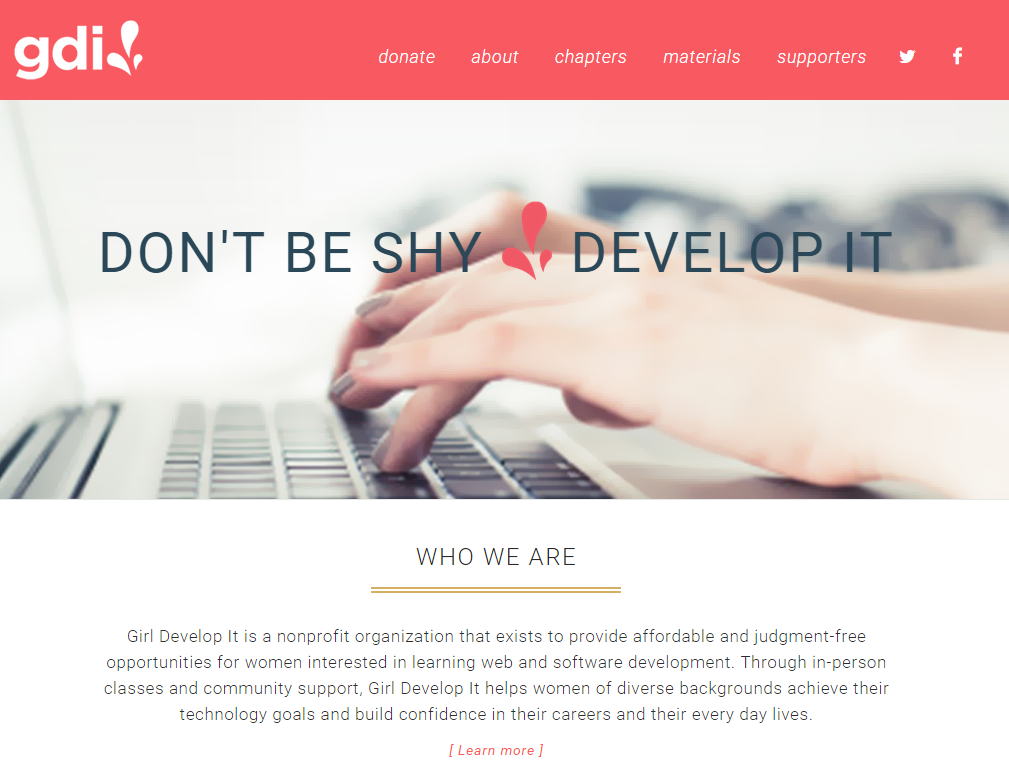
What is HTML?
If you 'view the source', you see this
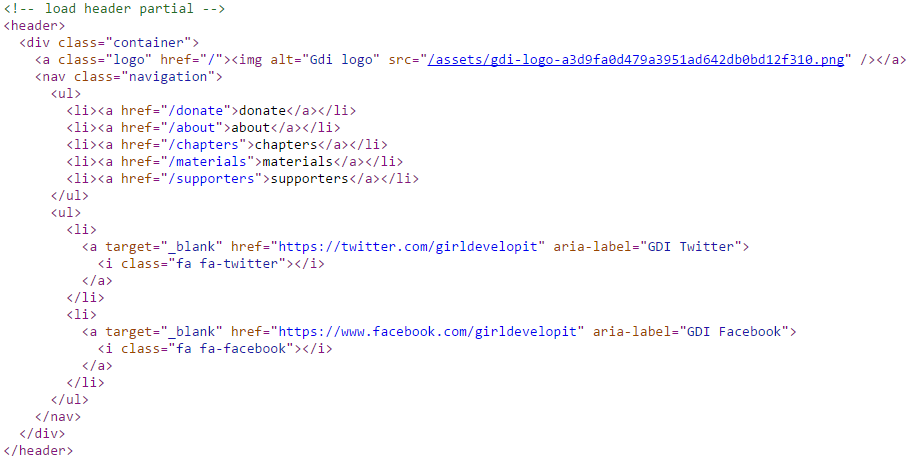
Anatomy of a website
Content: Text, Media
+ HTML: Structure + Semantics
+ CSS: Presentation + Design
+ JS: Interactivity
= Your Website
A website is a way to present your content to the world, using HTML and CSS to present that content & make it look good.
Anatomy of a website
Concrete example:
- A paragraph is your content
- Putting your content into an HTML tag to make it look like a paragraph is structure
<p>A paragraph is your content</p> - Making the font of your paragraph green and 24px is presentation
This paragraph is has been styled with CSS.
Tools
- Browser
Chrome
Firefox - Text Editor
Atom - Windows, Mac
Notepad++ - Windows
Sublime Text - Windows, Mac, Linux
TextWrangler - Mac
Get Started: Folder Structure
All the files for your site should be stored within the same folder.
This includes:
- HTML Files
- CSS Files
- Images
- Script files
- Anything else that will appear on your site
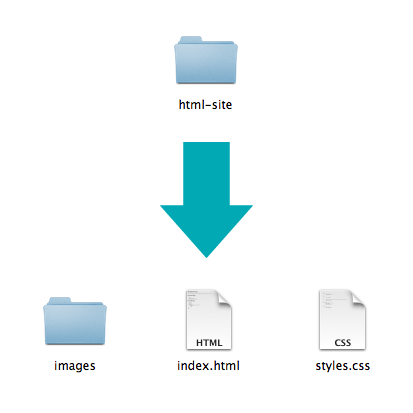
Naming Folders + Files
- Name your file
index.html - In file and folder names, only use lowercase letters, numbers, hyphens/dashes.
- File names are usually case sensitive:
INDEX.htmlvs.index.html - Use the right extension:
.htmlvs.cssvs.js
Let's Get Started!
- If you don't have an editor yet, download one.
- Create the folder for your website project.
- Open your text editor and create a new file. Save it inside your project folder as
index.html
Anatomy of an HTML element
HTML pages are made up of elements.
- Element
- An individual component of HTML
- Paragraph, heading, table, list, div, link, image, etc.
- Tag
- Marks the beginning & end of an element
- Tags contain characters that indicate the tag's purpose. Not all tags look the same.
Syntax:
<tagname>Content</tagname>Example:
<p>This is a sample paragraph.</p>Tag Breakdown

Doctype
The first thing on an HTML page is the doctype, which tells the browser which version of the markup language the page is using.
<!DOCTYPE html> * The doctype is case-insensitive.
DOCtype, doctype, DocType and DoCtYpe are all valid.
HTML Tag
After <doctype>, the page content must be contained between <html> tags.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
</html>
Head and Body Tags
head: Information about the page, like its title.
body: The actual content of the page, what shows up in the browser window.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>The title of the page</title>
</head>
<body>
The exciting content.
</body>
</html>
Head and Body Tags: Example
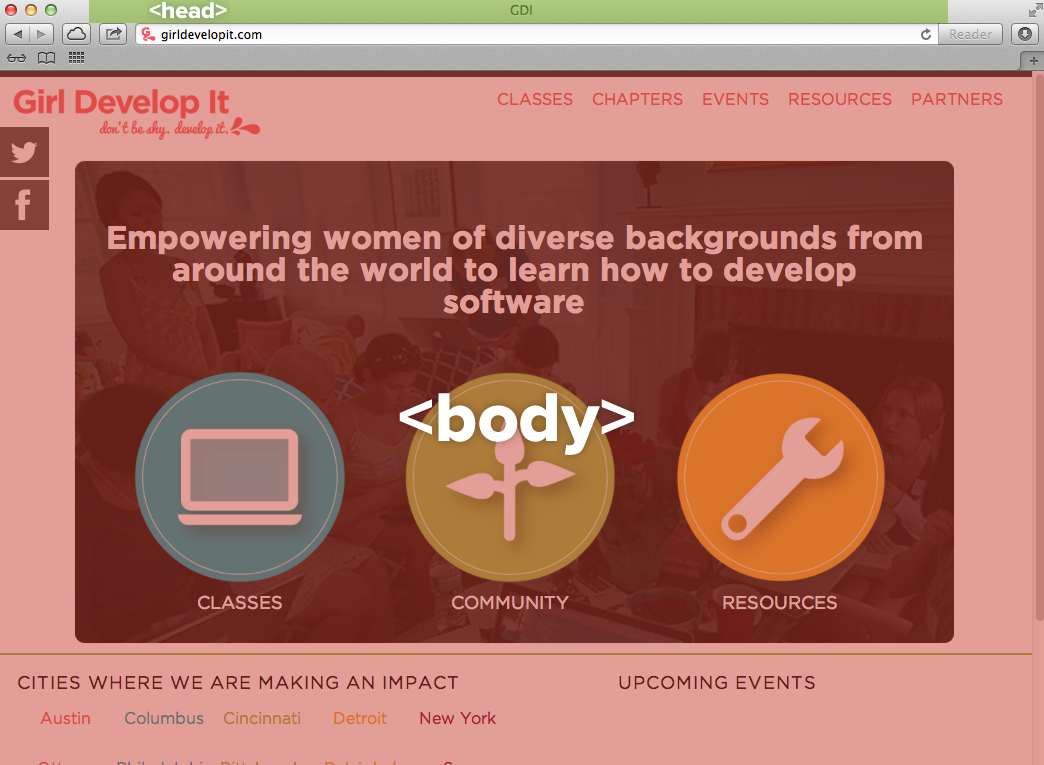
Meta tags
It's best practice to include meta tags that tells the browser the charset and viewport.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"/>
<title>Title of the page </title>
</head>
</html>
More reading: W3C: Declaring character encodings in HTML, Google PageSpeed: Configuring viewport
Nesting & Indentation
Elements "nest" inside the tag that contains them.
What elements are nested here?
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"/>
<title>Title of the page </title>
</head>
<body>
<p>A paragraph inside the body tag</p>
</body>
</html>
Notice: whichever element opens first, closes last.
Let's develop it!
Modify index.html to have all the tags that you just learned.
(You'll add content later!)
Paragraphs
Paragraphs allow you to format your content in a readable fashion.
* You can edit how paragraphs are displayed with CSS
Element: Paragraph
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
<p>Paragraph 3</p>
<p>Paragraph 1</p> <p>Paragraph 2</p> <p>Paragraph 3</p>
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
<p>Paragraph 3</p>
Paragraph 1
Paragraph 2
Paragraph 3
* White space is only for humans. You can write your code with any spacing.
Headings
Element: Heading
<h1>Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Heading 3</h3>
<h4>Heading 4</h4>
<h5>Heading 5</h5>
<h6>Heading 6</h6>
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
* Heading number indicates hierarchy, not size. Think of outlines from high school papers
Formatted text
<p>
This paragraph has <em>emphasized</em> text
and <strong>important</strong> text.
</p>
This paragraph has emphasized text and important text.
* Notice: em and strong are meant to indicate meaning through style. If you want to have italicized for appearance and not to communicate meaning, you should use CSS.
Let's Develop it!
You're going to make a page about your favorite food, animal, or activity.
- First you need text! You can either copy and paste from a Wikipedia article, or generate text from an Ipsum like Veggie Ipsum, Hipster Ipsum, Cupcake Ipsum.
- Add paragraph tags to break it into at least 3 paragraphs.
- Add formatting tags to emphasize "important" words.
- Add headings to describe your amazing paragraphs.
- Bonus: add fun characters from copypastecharacter.com.
Element Details: Attributes
- Attributes describe additional characteristics of an HTML element
- An attribute has 2 parts: name & value.
Syntax:
<tagname name="value">content</tagname>*Values should be contained inside quotation marks.
Element: Link
To make a link, you need 3 parts:
<a></a>taghrefattribute: web address where the link points- content: text or images between the tags that become the clickable link.
<a href="http://www.girldevelopit.com">Girl Develop It</a>
produces:
Girl Develop It
Link Targets
Optional target attribute tells the browser to open the link in a new tab.
<a href="home.html" target="_blank">Link Text</a>
More reading: Why external links should open in new tabs
Let's Develop It
Add 2 links that open in a new window.
Experiment!
- What about single versus double quotes?
- What happens if you forgot the " " around the
href?
Empty Elements
- Container Element
- An element that can contain other elements or content
<a href="http://example.com">A link element contains text.</a>
- An element that cannot contain anything else
<br/>
<img/>
Element: Line Break
<p>
Imagine there's no Heaven<br/>It's
easy if you try <br/>No hell below
us <br/>Above us only sky
</p>
Imagine there's no Heaven
It's easy if you try
No hell below us
Above us only sky
Element: Image
To make an image, you need 3 parts:
<img />tagsrcattribute: the location and name of the image filealtattribute: a brief description of the image content

<img src="img/circle-gdi-logo.png"
alt="Girl Develop It logo"/>

<img src="img/blinkylights.gif"
alt=""/>
More reading: When should alt text be blank?
Paths for Links & Images
Relative
Links within the same directory need no path information:<a href="filename.jpg">A file in same folder</a><a href="projects/another_file.html">A file from the projects folder</a>Absolute
Typically used when pointing to a link that is not within your own domain. Points to a specific location of a file, including the domain.<a href="http://www.girldevelopit.com/donate">Donate to GDI</a>Let's Develop It!
- Write a haiku about your webpage's topic and add line breaks to it.
- Add an image about your webpage's topic. Try using an absolute path (to an image online) and a relative path (to a downloaded image).
- Bonus: Try linking the image to an external page.
Lists
Lists can be used to organize any list of items.
You'd be surprised how often lists are used in web design.
Element: Unordered and ordered lists
<ul>
<li>List Item</li>
<li>Another List Item</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>List Item</li>
<li>Another List Item</li>
</ol>
Unordered list (bullets)
- List Item
- Another List Item
Ordered list (sequence)
- List Item
- Another List Item
Tables
Tables are a way to represent complex information in a grid format.
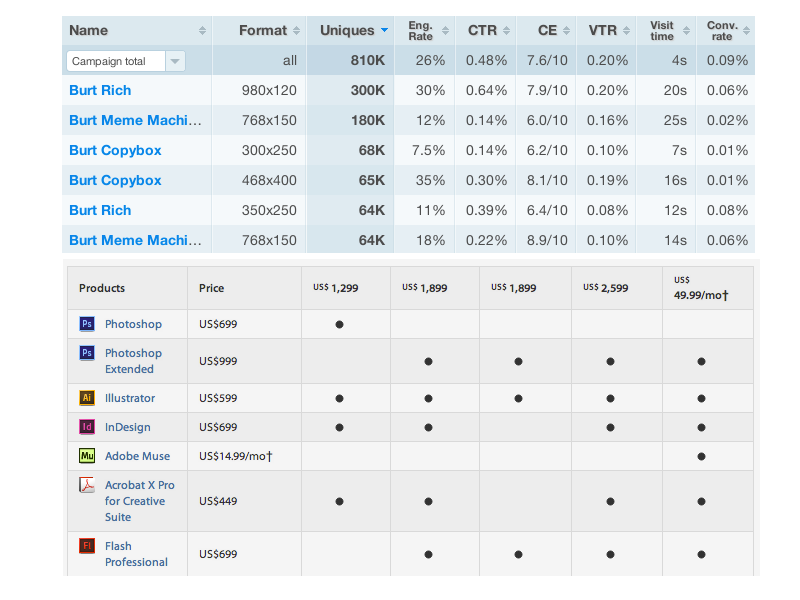
Element: Table
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Steph</td>
<td>Curry</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Tina</td>
<td>Fey</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
Tables are made up of header row(s) with the column names, and body rows with the data:
| First Name | Last Name |
|---|---|
| Steph | Curry |
| Tina | Fey |
Let's Develop it!
- Add one ordered list and one unordered list to your page.
- Add one table to your page.
- Bonus: Try putting other elements inside your table, like images and lists.
Comments
You can add comments to your code that will not be seen by the browser, but only visible when viewing the code.
<!-- Comment goes here -->
Comments can be used to organize your code into sections so you (or someone else) can easily understand your code. It can also be used to 'comment out' large chunks of code to hide it from the browser.
<!-- Beginning of header -->
<div id="header">Header Content</div>
<!-- End of header -->
<!--
<ol>
<li>List Item</li>
<li>Another List Item</li>
</ol>
-->